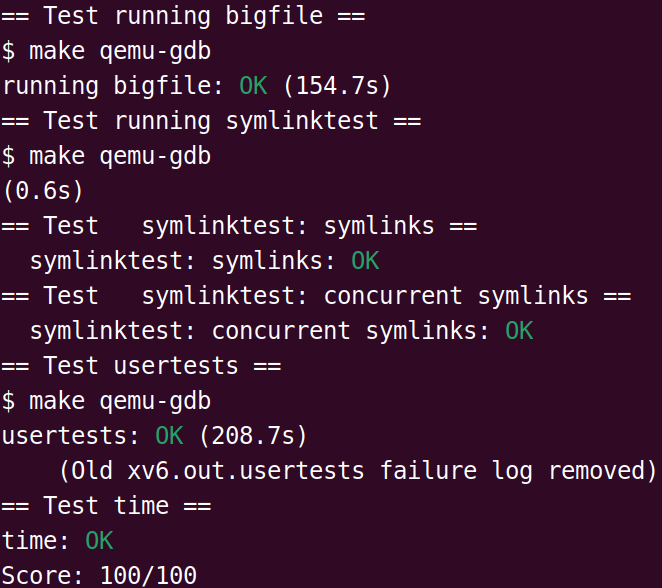
# Large files
增加对大文件的支持。原本系统中的一个目录表只有 12 个 direct inode 和 1 个 indirect inode,可存储的最大容量为 12+256 个 blocks,增加双重 indirect inode 后可扩容至 11+256+256*256 个 blocks。

原本一个 inode 目录支持 12 个直接 data 和一个 indirect 指针,为了给双重指针留出位置,需要减少一个直接 data。
//kernel/fs.h | |
#define NDIRECT 11 //-1 | |
#define NINDIRECT (BSIZE / sizeof(uint)) | |
#define DOUBLEDIRECT (NINDIRECT * NINDIRECT) // 双重指针支持的最大 size | |
#define MAXFILE (DOUBLEDIRECT + NINDIRECT + NDIRECT) // 汇总一个文件的最大 size |
修改相应结构体:
// fs.h | |
// On-disk inode structure | |
struct dinode { | |
short type; // File type | |
short major; // Major device number (T_DEVICE only) | |
short minor; // Minor device number (T_DEVICE only) | |
short nlink; // Number of links to inode in file system | |
uint size; // Size of file (bytes) | |
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2]; // Data block addresses +1 -> +2 | |
}; |
// file.h | |
// in-memory copy of an inode | |
struct inode { | |
uint dev; // Device number | |
uint inum; // Inode number | |
int ref; // Reference count | |
struct sleeplock lock; // protects everything below here | |
int valid; // inode has been read from disk? | |
short type; // copy of disk inode | |
short major; | |
short minor; | |
short nlink; | |
uint size; | |
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2]; // +1 -> +2 | |
}; |
修改 bmap 映射函数和 itunc 清理函数:
// fs.c | |
static uint | |
bmap(struct inode *ip, uint bn) | |
{ | |
uint addr, *a, *b; | |
struct buf *bp, *bp2; | |
if(bn < NDIRECT){// 直接映射 | |
// ... | |
} | |
bn -= NDIRECT;// 直接映射的 11 个 block 填充完毕 | |
if(bn < NINDIRECT){// 一级指针映射 | |
// ... | |
} | |
bn -= NINDIRECT;// 一级映射的 256 个 block 填充完毕 | |
if(bn<DOUBLEDIRECT){// 二级指针映射 | |
//middle layer | |
if((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1]) == 0){// 获取二级指针地址 | |
addr = balloc(ip->dev);// 分配二级指针地址 | |
if(addr == 0) | |
return 0; | |
ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1] = addr; | |
} | |
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr); | |
a = (uint*)bp->data;// 一级指针表 | |
if((addr = a[bn/NINDIRECT]) == 0){// 存到哪一个一级指针对应的二级指针表 | |
addr = balloc(ip->dev); | |
if(addr){ | |
a[bn/NINDIRECT] = addr; | |
log_write(bp); | |
} | |
} | |
brelse(bp); | |
//end layer | |
bp2=bread(ip->dev,addr); | |
b=(uint*)bp2->data;// 二级指针表 | |
if((addr=b[bn%NINDIRECT])==0){// 存到二级指针表中对应的哪一个块 | |
addr = balloc(ip->dev); | |
if(addr){ | |
b[bn%NINDIRECT]=addr; | |
log_write(bp2); | |
} | |
} | |
brelse(bp2); | |
return addr; | |
} | |
panic("bmap: out of range"); | |
} | |
void | |
itrunc(struct inode *ip) | |
{ | |
int i, j; | |
struct buf *bp,*bp2; | |
uint *a,*b; | |
for(i = 0; i < NDIRECT; i++){ | |
// ... | |
} | |
if(ip->addrs[NDIRECT]){ | |
// ... | |
} | |
if(ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1]){// 清理二级指针 | |
bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1]); | |
a = (uint*)bp->data; | |
for(j = 0; j < NINDIRECT; j++){// 获取指针表的每一项 | |
if(a[j]){ | |
bp2 = bread(ip->dev, a[j]); | |
b = (uint*)bp2->data; | |
for(int k=0;k<NINDIRECT;k++){// 获取指向的 block | |
if(b[k]) | |
bfree(ip->dev, b[k]); | |
} | |
brelse(bp2); | |
} | |
} | |
brelse(bp); | |
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1]); | |
ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1] = 0; | |
} | |
ip->size = 0; | |
iupdate(ip); | |
} |
# Symbolic links
增加软链接功能,例如执行 symlink (‘a’,‘b’) 后,打开’b’的指令会实际打开’a’。
增加系统调用的方法与之前类似,修改 syscall 列表,usys.pl,MakeFile(增加 symlinktest 而非 symlink)等。
按照提示在 fcntl.h 中增加标志位,0x800 与前面的标志进行 “或” 运算时不冲突,不会覆盖其它标志位。
#define O_RDONLY 0x000 | |
#define O_WRONLY 0x001 | |
#define O_RDWR 0x002 | |
#define O_CREATE 0x200 | |
#define O_TRUNC 0x400 | |
#define O_NOFOLLOW 0x800 //new added |
主要是实现软连接函数和修改 open 文件的逻辑:
uint64 | |
sys_symlink(void){ | |
char target[MAXPATH], path[MAXPATH]; | |
struct inode *ip; | |
if(argstr(0, target, MAXPATH) < 0 || argstr(1, path, MAXPATH) < 0) | |
return -1; | |
begin_op(); | |
if((ip = namei(path)) != 0){//already exist | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
ip=create(path,T_SYMLINK,0,0);// 给 symlink 分配一个 inode | |
if(ip==0){ | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
if(writei(ip,0,(uint64)target,0,MAXPATH)<0){ // 将目标地址写入新分配的 inode | |
iunlockput(ip); | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
iunlockput(ip); | |
end_op(); | |
return 0; | |
} | |
uint64 | |
sys_open(void) | |
{ | |
char path[MAXPATH]; | |
int fd, omode; | |
struct file *f; | |
struct inode *ip; | |
int n; | |
argint(1, &omode); | |
if((n = argstr(0, path, MAXPATH)) < 0) | |
return -1; | |
begin_op(); | |
if(omode & O_CREATE){ | |
ip = create(path, T_FILE, 0, 0); | |
if(ip == 0){ | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
} else {// | |
int depth=0;// 递归深度 | |
if((ip = namei(path)) == 0){ | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
ilock(ip); | |
if(ip->type == T_DIR && omode != O_RDONLY){// 这个判断必须保留 | |
iunlockput(ip); | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
while(ip->type==T_SYMLINK && !(omode & O_NOFOLLOW)){// 是软链接 | |
if(readi(ip,0,(uint64)path,0,MAXPATH)<0){// 读取存储的路径 | |
iunlockput(ip); | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
iunlockput(ip); | |
if((ip = namei(path)) == 0){// 获取路径对应的 inode | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
ilock(ip); | |
if(++depth>10){// 数值随意取,能防止递归自环的合理值 | |
iunlockput(ip); | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
// 以下不变 | |
if(ip->type == T_DEVICE && (ip->major < 0 || ip->major >= NDEV)){ | |
iunlockput(ip); | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
if((f = filealloc()) == 0 || (fd = fdalloc(f)) < 0){ | |
if(f) | |
fileclose(f); | |
iunlockput(ip); | |
end_op(); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
if(ip->type == T_DEVICE){ | |
f->type = FD_DEVICE; | |
f->major = ip->major; | |
} else { | |
f->type = FD_INODE; | |
f->off = 0; | |
} | |
f->ip = ip; | |
f->readable = !(omode & O_WRONLY); | |
f->writable = (omode & O_WRONLY) || (omode & O_RDWR); | |
if((omode & O_TRUNC) && ip->type == T_FILE){ | |
itrunc(ip); | |
} | |
iunlock(ip); | |
end_op(); | |
return fd; | |
} |
# Test